DISCLAIMER: THIS CONTENT IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. IT IS NOT A RECOMMENDATION TO PURCHASE TOKENS OR ANY OTHER ASSETS. ANY INVESTMENTS MADE IN THE PROJECTS OR ASSETS MENTIONED BELOW ARE DONE SO AT YOUR OWN RISK. THIS IS NOT FINANCIAL ADVICE.
Art and collectible markets generally suffer from less liquidity than fiat, equity, or other types of assets. This dynamic is also true in NFT markets as they are still in their infancy, with most activity based purely on speculation. And after a crazy period of buying, selling, and trading NFTs during the previous bull cycle, investors now seek new ways to leverage their assets. New and exciting projects go live everyday, but with many NFT gamers and collectors tied up in NFTs already, the liquidity issue becomes especially acute during this period of financial tightening across all sectors.
???? NFTFi was born from the idea of combining DeFi and NFTs to attract new investors and increase liquidity for current participants. NFTFi platforms allow owners to earn real yield from their NFTs, instead of letting them sit idle in their crypto wallets.
What makes NFTFi Useful?
Let’s say, for example, you own an NFT that you plan on holding long term. If it’s from a popular “blue-chip” collection, you’ve locked up a significant amount of capital in that jpeg and without easy access. What if you got in an accident or urgently need cash for some other opportunity? You could be forced to sell at a loss, or instead use NFTFi to unlock some percent of the total value without relinquishing ownership (unless you were to later default on repaying the loan). This presents a great opportunity for lenders to earn some yield while giving NFT holders access capital in a pinch. And for the skilled investor, this creates an exciting opportunity to put those NFT collections to work.

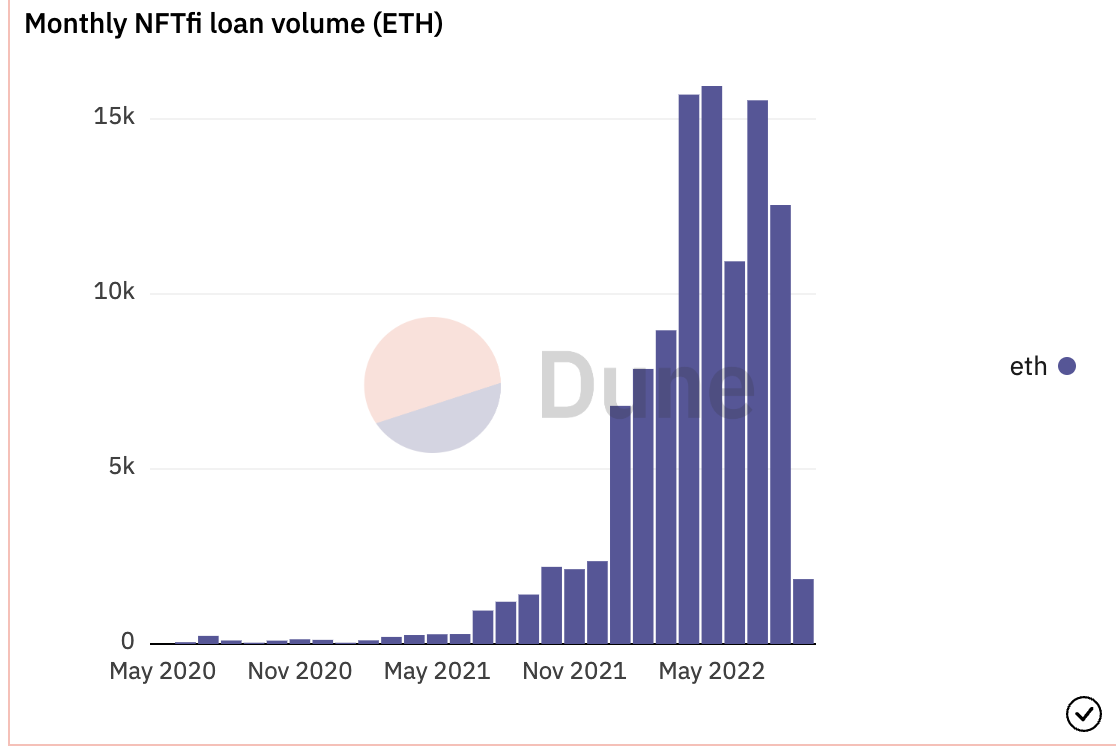
NFTFi All-time Loan Volume by Collateral (Source: The Block Research)
Per the data above, Blue-Chip NFTs (BAYC, Cryptopunks, Art Blocks, etc) are favored both by borrowers and lenders for obvious reasons. Many if not most BAYC and punk owners do not actively trade their NFTs, choosing to enjoy them for their collectible and social value, among other benefits.
Game NFT markets tend to be more or less liquid depending on how popular and active the game’s player base is, which has been correlated with market conditions in this first cycle as many owners were speculators rather than loyal players. We anticipate this trend will change as more fun games with sustainable token economies are released.
What is NFTFi? When NFT meets DeFi
Use the NFTs you own to access the liquidity you need - nftfi.com

Source: nfttech.com
NFTFi (NFT + DeFi) is a set of liquidity protocols that enable NFT to finance transactions by accessing more liquid assets in a completely trustless manner with the help of smart contracts.
NFTFi ecosystem will also enable NFT collectors optimize their cash flow, generating additional incentive for them to buy and hold NFT as an asset class with long-term potential rather than a means for speculative facilities.
What are the current sectors within NFTFi?
There are a variety of sectors within NFTFi, including some popular ones, with their respective pros and cons:
- Lending\Borrowing using NFTs
- NFT Renting
- NFT Fractionalization
- NFT Derivatives
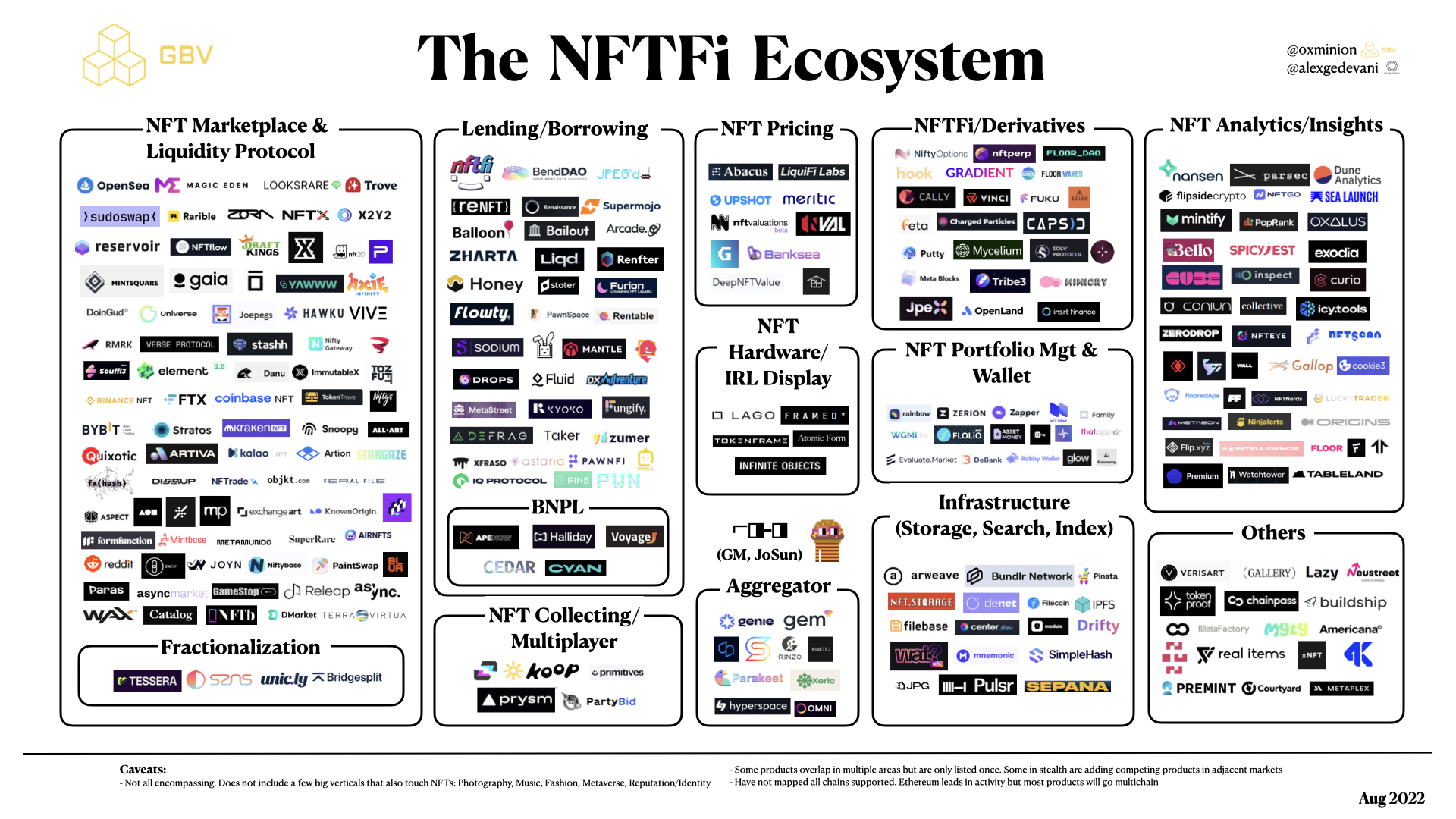
The NFTFi Ecosystem and its associated platforms
Lending/Borrowing using NFTs
NFT lending is a growing sector within the NFT industry. Like DeFi lending, NFT lending is the act of collateralizing your NFT in exchange for immediate access to a crypto loan, usually facilitated on-chain via a smart contract. The smart contract contains the assets, the liquidity (loan), and the terms and conditions of the loan.
Per our initial, hypothetical example, this combination of DeFi and NFTs has opened up convenient and exciting of possibilities for NFT holders by making their NFTs more “liquid.”
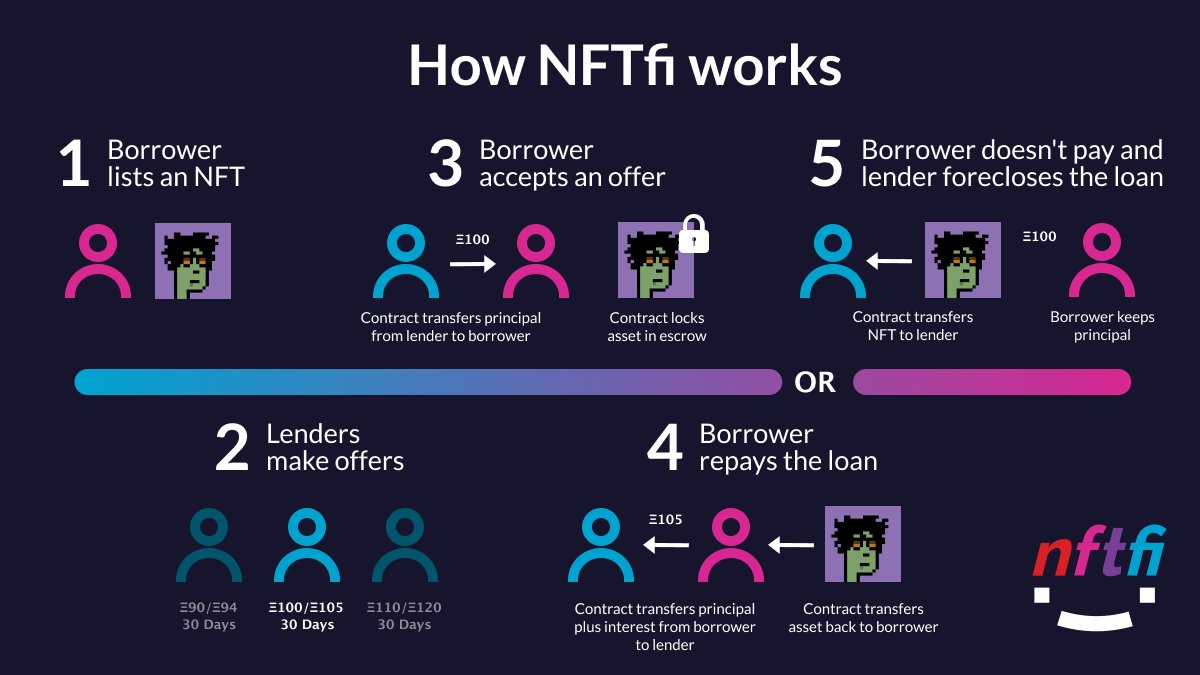
Source: @NFTI/TWITTER - A typical process how to lend an NFT on nftfi.com
A quick analysis Benefits and Risks of participating in NFTFi (lending / borrowing sector)
| Lenders (Liquidity Providers) | Borrowers (NFT Owners) | |
| Benefits | - Liquidity providers use their idle capital to earn attractive yield. - If a Borrower defaults, they have a chance to obtain the NFT at a steep discount to market prices. Strategies vary among liquidity providers. |
- NFT owners may deposit or send their NFT as collateral to borrow a corresponding amount of $ETH. |
| Risks |
- Loan-to-value ratio: - NFT price volatility:
|
- Liquidation of NFT assets After the user repays the loan, the property is transferred back. If the user is unable to repay the loan before the due date, the property goes to the lender. |
NFT Lending / Borrowing Process:
- The NFT asset that you choose to use as collateral is sent to a NFTFi escrow smart contract.
- Potential lenders make offers; if you accept an offer then your asset is locked in the smart contract and your wallet will receive the loaned $ETH (or other cryptocurrency).
- Per the agreed upon terms, you must repay the loan plus interest to recover the NFT assets you staked as collateral.
- If you don’t repay the loan in time, your NFT becomes available for foreclosure by the lender.
- Note that if the lender does foreclose, then the NFT will be transferred to their wallet. Because it is a non-recourse loan, the origination fee and loan amount are waived.
| Pros | Cons |
|
NFT lending provides additional liquidity support to the whole NFT ecosystem. This new industry allows NFT lenders to leverage their collections to earn yield, which is paid by the borrower, in the form of loan interest. Borrowers also have the option to finance new NFT purchases through loans, as they can access more liquid capital without having to sell their NFT. Due to the volatility of crypto and NFT markets, this must be considered a high-risk endeavor. |
Difficulty in pricing an NFT: Platforms have different mechanisms to price NFTs, from simply using floor price or using their own pricing oracle. Using floor price can severely undervalue the NFT, though, as the floor price is equal to the least valuable NFT listed in a collection. The oracle pricing mechanisms are also problematic, as their methods are extremely opaque and their accuracy, questionable. To mitigate this issue, currently, most platforms only allow certain NFT collections to be used as collateral, guaranteeing some degree of stability in the price of collateral for those who provide loans. |

NFT collections that are accepted as collateral. (Source: The Block Research)
Every financial market will bring both benefits and risks. Users need to understand what they are doing, especially in the blockchain-based financial market.
As a borrower (Liquidity Providers), it is important to remember this is still a new sector. All the terms, such as loan value, interest, and duration of the loan, are set by the lender or smart contracts. And if you’re not happy with the terms, then don’t accept the crypto loan. The bottom line is that every party involved is in control of their own risk!
As a lender (NFT owners), researching the NFT offered as collateral is key. Because if the borrower defaults, you will most likely be looking to consider selling or holding the NFT asset, and if you do not understand the value of the NFT, then it’s probably a loss!
What is NFT Renting?

What is NFT Rental? (Source: tokenizedhq.com)
Imagine you own an NFT that has utility (especially game NFT). You can either use that utility yourself or you can rent NFTs out to someone else for a fee.
NFT renting gives you the benefits of having an NFT without the financial commitment of investing in it.
NFT Renting process:
- An NFT owner lists their asset on a rental marketplace. The renter can then initiate the renting process.
- The NFT is placed in a smart contract with the terms and conditions of the borrower and the lender to enable safe transactions. These conditions include the rental fee and collateral, which has a higher price than the NFT to protect the lender.
- After the contract expires or the renter no longer has demand, the NFT and the collateral are returned to their original owners.
| Pros | Cons |
| - Earn passive income from NFT on their own terms, without having to concern themselves with fractionalization problems. - Access to NFT-gated events of communities for a period of time, if they’re not using them for that purpose themselves, but wish to retain exposure to the NFT. |
NFT renting is still a new business model in the world of NFTs, and is therefore prone to exploits. One recent exploit occurred during the ApeCoin airdrop to BAYC holders. An unknown user took a flash loan and rented out 5 BAYC NFTs before the airdrop to make his/her wallet eligible for the ApeCoin airdrop. They were airdropped ApeCoin, and the unknown user managed to make $800,000 because of a NFT renting exploit. |
Over-Collateralized Renting
A prospective renter can gain access to the NFT they want to borrow by posting collateral valued at a higher price than the borrowing NFT price. Borrowers can then access the NFT for a period of time specified by the NFT holder and the encoded smart contract to which the NFT is tied.
Under-Collateralized Renting
The key different: Renter only receive a wrapped version of the original NFT with the same utility.
Platforms that offer Under-collateralized renting allow lenders to deposit their NFT and make a wrapped version of it. Once a user rents the NFT and pays the rental fee, the renter receives the wrapped NFT and enjoys the same utility as the original. After the contract expires, the wrapped NFT is burned, and the rental fee sent to the lender.
???? Under-collateralized renting minimizes risk for both parties since the renter doesn’t need to put up collateral and the lender doesn’t need to rent out their original asset.
What is NFT Fractionalization?

NFT Fractionalization
Fractionalization is the act of dividing an NFT into smaller fractionalized pieces to be sold and traded on a public or private marketplace. The process helps share ownership of an NFT through a set of fungible tokens tied to the original NFT. This topic will be explored in greater detail in a future article on the Ancient8 Research Portal.
| Pros | Cons |
| NFT fractionalization enables access to valuable NFTs that are too expensive for average investors. Ownership is divided and represented by more affordable shares using fungible tokens. This makes NFT ownership more accessible and can create a more liquid market for expensive NFTs. | In order to get your NFT out of the vault, all shares of the fractionalized NFT must be sold. The process of “putting it back together” can be difficult and time consuming. |
What are NFT Derivatives?

NFT derivatives are a product that lets users bet on the future prices of an NFT. It is a kind of speculating the price on the future date.
Derivatives trading is nothing new when it comes to traditional crypto assets listed on an exchange. The same concept applies to NFTs: to provide a platform for retail users and traders to take long or short positions on the value of NFTs, thereby enabling more robust trading strategies that can maximize profit opportunities for users while hedging risk and exposure.
| Pros | Cons |
| - Opens a lot of possibilities in terms of NFT liquidity in terms of using leverage to trade NFTs. - The derivatives market in TradFi is significantly bigger than spot markets, showing potential for the NFT market growth with NFT derivatives |
- NFT derivatives are highly risky, especially when using leverage, as it can magnify losses. Higher risk means higher rewards, and losses. - Only a few top NFT collections are currently available for derivatives trading. |
Final thoughts
NFT Finance is a complementary instrument which we believe is necessary to help NFT markets reach broader capital. It has the potential to play a critical role in providing NFTs with the elements required for the space to be broadly acknowledged as an asset class.
These new financial instruments, whether financial primitives or more complex 'money legos’, can directly unlock novel value flows for both existing and new market players.





















